Summary
- Predictive maintenance software leverages real-time data and AI to forecast equipment failures before they occur, shifting from reactive to proactive maintenance.
- Adopting these tools can reduce machine downtime by up to 50% and extend machine life by up to 40%, significantly impacting the bottom line.
- Key technologies driving this shift include IoT predictive maintenance tools, vibration analysis sensors, and machine learning algorithms that detect anomalies early.
- Successful implementation requires overcoming data silos and cultural resistance, moving away from “run-to-failure” mindsets toward data-driven decision-making.
- Modern solutions integrate seamlessly with existing maintenance management software (CMMS) to automate work orders and streamline industrial operations.
Introduction
Unplanned downtime is the industrial equivalent of a root canal: painful, expensive, and usually happening at the worst possible moment. According to a report by Aberdeen Strategy & Research (2023), the average cost of unplanned downtime across all manufacturing sectors has surged to roughly $260,000 per hour. That is a staggering figure. For a semiconductor plant or a high-volume automotive line, a single stopped conveyor belt burns through capital faster than a furnace.
This financial hemorrhage explains why reliability engineers are scrambling to adopt predictive maintenance software. The era of crossing your fingers and hoping the motor lasts until the next scheduled shutdown is over. By utilizing advanced algorithms and sensor data, modern platforms provide a window into the future health of your assets. It is no longer about fixing things when they break; it is about knowing they will break three weeks from Tuesday.
The industrial landscape is shifting toward data-driven reliability. Facilities that ignore this transition risk will be left behind with their clipboards and grease guns. This guide explores how predictive maintenance software works, the ROI it delivers, and why it has become the backbone of smart manufacturing.
From Reactive Chaos to Intelligent Prediction
To understand the value of predictive tools, we must look at the evolution of maintenance strategies. For decades, the industry operated on two primary models: reactive and preventive.
The Old Ways: Run-to-Failure and Preventive
Reactive maintenance is simple: run the machine until smoke comes out, then fix it. While this requires zero planning, the catastrophic costs of emergency repairs and lost production make it unsustainable for critical assets.
Preventive maintenance (PM) was the first step toward sanity. This involves servicing equipment on a fixed schedule, like changing your car’s oil every 5,000 miles. It works, but it is inefficient. You might replace a perfectly good bearing simply because the calendar says so. This leads to wasted parts and unnecessary labor.
The New Standard: Condition-Based Maintenance
Predictive maintenance software changes the trigger from “time” to “condition.” It relies on condition monitoring software to assess the actual health of the machine.
Imagine if your car didn’t tell you to change the oil based on mileage, but instead analyzed the viscosity and particulate matter in the oil every second, alerting you the moment it degraded. That is the essence of predictive analytics. It maximizes the useful life of a component while preventing it from failing.
The Mechanics: How the Software Works
It might seem like magic, but it is purely math and physics. The software acts as the central brain, processing streams of data from the factory floor.
The Eyes and Ears: IoT and Sensors
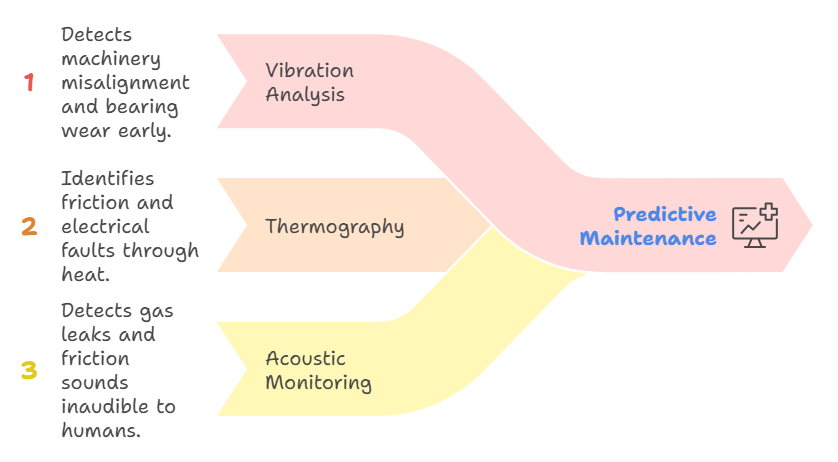
The process begins with IoT predictive maintenance tools. Sensors attached to equipment measure various physical parameters.
Vibration Analysis: The most common method for rotating machinery. Changes in vibration patterns often indicate misalignment or bearing wear weeks before failure.
Thermography: Heat is a telltale sign of friction or electrical faults.
Acoustic Monitoring: Sonic and ultrasonic sensors detect gas leaks or friction sounds inaudible to human ears.
These sensors feed data into industrial asset monitoring systems continuously.
The Brain: AI and Machine Learning
Raw data is useless without interpretation. This is where AI maintenance software steps in. The software establishes a baseline for “normal” operation. When a data point deviates from this baseline, perhaps a motor is vibrating 2% more than usual, the AI flags it.
Sophisticated algorithms compare these anomalies against historical failure data. The system might flag an alert: “85% probability of bearing seizure in Motor 3 within 14 days.”
The Business Case: ROI and Benefits
Why should a CFO sign off on this investment? The answer lies in the numbers. According to Deloitte (2022), predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by 25%, lower breakdowns by 70%, and reduce downtime by 50%.
Slash Unplanned Downtime
The most direct benefit is keeping the line running. By catching issues early, maintenance teams can schedule repairs during planned outages or shift changes. This prevents the “2:00 AM emergency call” that every plant manager dreads.
Optimize Spare Parts Inventory
Maintenance management software linked with predictive tools allows for “just-in-time” inventory. Instead of stocking expensive motors “just in case,” you order them when the software indicates a decline in asset health. This frees up working capital previously tied up in dusty warehouse shelves.
Enhanced Worker Safety
Catastrophic failures are dangerous. A boiler explosion or a high-speed belt snap puts lives at risk. Industrial predictive maintenance keeps equipment within safe operating limits, protecting the workforce from mechanical hazards.
Key Features of Top-Tier Software
When evaluating vendors, look for these specific capabilities to ensure the system can handle the rigors of your facility.
Real-Time Equipment Monitoring and Edge Computing
Cloud processing is great, but latency can be an issue. The best solutions often employ edge computing, processing critical data directly on the device (the “edge”) for instant alerts. Real-time equipment monitoring ensures that if a critical threshold is breached, the shut-off signal is immediate.
Seamless CMMS Integration
Your predictive tool should not be an island. It must talk to your CMMS predictive maintenance module. When an anomaly is detected, the software should automatically generate a work order in the CMMS, complete with the diagnostic data and recommended repair actions. This removes the manual step of a human having to interpret a graph and type out a request.
Scalability and Asset Agility
You might start with ten critical motors, but you will eventually want to monitor hundreds of assets. Ensure the licensing and architecture support scaling without requiring a complete system overhaul.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite the clear benefits, adoption isn’t always smooth. It requires a culture shift as much as technology.
The Data Silo Problem
Many factories suffer from fragmented data. The SCADA system doesn’t talk to the ERP, and the maintenance logs are on paper. Industrial IoT maintenance solutions serve as the bridge, but cleaning and normalizing this data is often the hardest part of the project.
The “Experienced Mechanic” Factor
There is often pushback from veteran staff who prefer “percussive maintenance” (hitting it with a wrench) or who trust their gut over a computer.
Overcoming this requires training and showing the team that the software is a tool to make their lives easier, not a replacement for their expertise.
Industry Use Cases
Semiconductor Manufacturing
In wafer fabrication, precision is everything. A slight vibration in a vacuum pump can ruin a batch of chips worth millions. Einnosys understands that in this sector, machine health monitoring must be hyper-sensitive. Predictive tools track the degradation of electrostatic chucks and robot arms to ensure yield remains high.
Automotive and Heavy Industry
For automotive plants using thousands of robotic arms, maintenance automation software is critical. Predicting servo motor failure on a welding robot prevents the entire assembly line from halting, ensuring the “one car per minute” target remains viable.
The Future: Generative AI and Digital Twins
The next frontier is the integration of Generative AI. Instead of reading a graph, you might soon ask your predictive analytics for maintenance system, “What is the health status of Line 4?” and receive a conversational summary.
Furthermore, Digital Twin technology allows engineers to create a virtual replica of a machine. They can run simulations on the twin to see how increased load might affect lifespan, helping refine maintenance schedules without risking the physical asset.
Conclusion
Ultimately, adopting predictive maintenance software is no longer a futuristic luxury but a fundamental necessity for staying competitive in the modern industrial landscape. By pivoting from reactive “firefighting” to data-driven foresight, manufacturers can unlock massive value, slashing unplanned downtime, extending asset lifecycles, and empowering teams to work smarter, not harder. The days of crossing your fingers and hoping a machine lasts are over; the future belongs to facilities that listen to their data to ensure reliability and operational excellence.
FAQs
-
What is the difference between preventive and predictive maintenance?
Preventive maintenance is schedule-based (e.g., every month), regardless of the machine's condition. Predictive maintenance is condition-based, meaning maintenance is performed only when data indicates a decline in performance or an impending failure.
-
Does predictive maintenance software require new sensors?
Often, yes. While some modern equipment comes with built-in sensors, older legacy machines usually require retrofitting with external vibration, temperature, or acoustic sensors to feed data into the IoT predictive maintenance tools.
-
Can this software integrate with my existing CMMS?
Yes, most enterprise-grade predictive platforms are designed to integrate via API with major CMMS providers (like SAP, Maximo, or specialized maintenance tools), enabling automated work order generation.
-
What industries benefit most from industrial predictive maintenance?
Industries with high downtime costs or critical safety requirements benefit most. This includes semiconductor manufacturing, oil and gas, power generation, automotive, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
📅 Posted by Nirav Thakkar on December 2, 2025
Nirav Thakkar
Semiconductor Fab Automation & Equipment Software specialist with 18 years of industry experience.

