
Summary
- Predictive maintenance (PdM) is an industrial strategy that uses condition monitoring and data analytics to anticipate equipment failure.
- The global industrial predictive maintenance market is set to grow from $7.9 billion in 2023 to $32.4 billion by 2032, driven by the need for efficiency and cost savings (Precedence Research, 2024).
- PdM moves operations beyond reactive or time-based maintenance, significantly reducing downtime and lowering overall maintenance costs.
- Key benefits include enhanced equipment health monitoring, increased asset lifespan, optimized resource allocation, and a direct contribution to industrial profitability.
- Adopting PdM is crucial for industries aiming for operational excellence and thriving in the competitive landscape of Industry 4.0.
Introduction
For too long, industrial maintenance has been a reactionary, high-stress endeavor. Plant managers and engineers often found themselves playing “catch-up,” rushing to fix broken machinery after a breakdown had already halted production and wreaked havoc on schedules. This reactive approach is incredibly costly, not just in parts and labor, but in the lost revenue from unexpected downtime.
The modern industrial landscape, however, demands a shift. According to Precedence Research (2024), the global industrial predictive maintenance market size is expected to reach $32.4 billion by 2032, showcasing a strong industry-wide pivot toward smarter operational strategies. This staggering growth projection confirms one thing: the era of reactive maintenance is ending, and the age of foresight has begun.
This article explores why predictive maintenance is unequivocally the key solution for sustainable industrial growth. By transitioning from scheduled guesswork to data-driven insights, businesses can not only minimize catastrophic failures but also fundamentally transform their operational efficiency and bottom line.
The Economics of Foresight: Why PdM is Profitable
The primary allure of predictive maintenance isn’t just that it prevents breakdowns; it’s that it optimizes the entire maintenance lifecycle. Unlike the “fix-it-when-it-breaks” mentality (reactive) or the “replace-it-whether-it-needs-it-or-not” approach (preventive), PdM ensures that maintenance is performed at the precise moment it is most needed. This switch delivers a massive return on investment (ROI).
Rastically Reducing Downtime and Costs
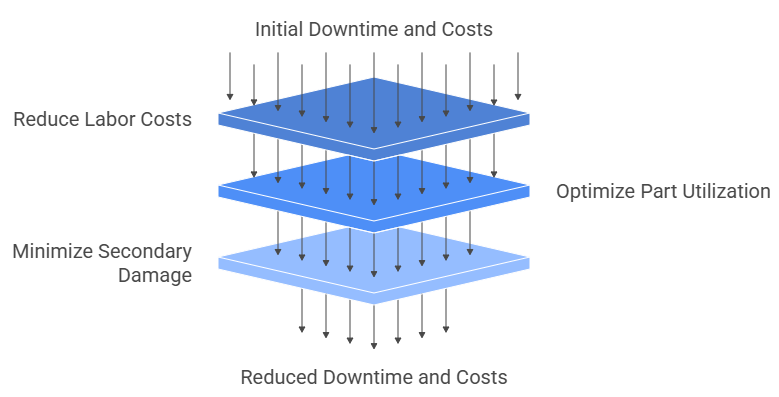
The most immediate and substantial benefit of PdM is the reduction in unexpected production outages. Unplanned downtime can cost manufacturers hundreds of thousands of dollars per hour, depending on the industry and the scale of the operation.
Reduced Labor Costs: By scheduling maintenance precisely, teams can minimize overtime and emergency call-outs, focusing their efforts during planned, efficient windows.
Optimal Part Utilization: With PdM, components are replaced based on actual wear and tear, not an arbitrary calendar date. This drastically reduces inventory holding costs for unnecessary parts, saving capital expenditure. McKinsey (2020) estimates that condition-based maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by 10% to 40% compared to traditional approaches.
Minimized Secondary Damage: A small, unnoticed fault (like a bearing vibration) can quickly cascade into a catastrophic failure that destroys an entire machine. Industrial predictive maintenance flags these minor issues early, allowing a small, targeted repair to prevent a massive, expensive replacement job.
Think of it this way: traditional maintenance is like changing your car’s oil every 5,000 miles, even if you’ve driven only on the highway. PdM is like changing it based on a sensor that monitors the actual oil degradation. Which approach sounds smarter for your bank account?
Powering Industrial Growth with Data-Driven Decisions
Industrial growth solutions are no longer about simply buying bigger machines; they’re about making existing assets work smarter and longer. Predictive maintenance technology is the backbone of this strategy, transforming raw operational data into actionable business intelligence.
Leveraging the Ecosystem of Industry 4.0
PdM is intrinsically linked to Industry 4.0, utilizing interconnected technologies to create a “smart factory.” These systems constantly monitor the health of critical assets.
The Role of IoT and AI in Maintenance
The digital infrastructure supporting PdM relies on a powerful combination of sensors and advanced analytics:
IoT in Industrial Maintenance: Thousands of sensors measuring vibration, temperature, acoustic emissions, and motor current are installed on equipment. These Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices collect massive streams of data about the machine’s performance in real time.
Predictive Analytics for Maintenance: This data is fed into sophisticated AI/ML developers’ models. The machine learning algorithms analyze historical failure data against current operating conditions to learn the unique “signature” of a healthy machine and, crucially, the subtle deviations that signal impending failure.
Smart Maintenance Systems: These platforms translate the model’s prediction into an alert, often calculating the “Days to Failure” or “Probability of Failure.” This intelligence allows a maintenance manager to schedule an intervention weeks in advance, eliminating the element of surprise.
Instead of guessing, maintenance teams receive precise instructions: “The pump’s bearing on line 3 is showing a 95% probability of failure within the next 14 days.” This level of certainty changes everything.
Improving Safety and Asset Lifespan
Beyond cost savings, PdM contributes to a safer, more reliable operating environment.
Catastrophic equipment failures don’t just cost money; they pose significant risks to personnel. By preventing violent machinery breakdown, such as exploding pressure vessels or collapsing conveyor belts, PdM enhances workplace safety. Furthermore, operating machinery within its optimal parameters, rather than pushing it to the point of failure, extends its useful life. This is a critical factor for CFOs and CTOs who are focused on long-term capital expenditure planning. Maximizing the lifespan of high-value assets defers significant reinvestment costs.
What’s the point of running a piece of equipment to death when a little foresight can add years to its operational life?
Overcoming Barriers to PdM Adoption
While the benefits are clear, the transition to a modern maintenance 4.0 strategy requires commitment, particularly in areas like data infrastructure and team training.
Challenges in Implementation and Strategy
The initial investment in sensors, networking infrastructure, and predictive maintenance software companies can seem daunting. For many facility managers, the shift from familiar, paper-based routines to a digital, data-driven system is a cultural hurdle.
Integration Complexity: Connecting legacy operational technology (OT) systems with modern information technology (IT) networks is a common challenge. Data needs to flow seamlessly from the shop floor to the cloud analytics platform.
Data Science Skill Gap: Implementing an AI in a maintenance system requires more than just installing software. It needs skilled personnel, either in-house data scientists or external partners, to interpret the output, refine the models, and manage the underlying data architecture.
Change Management: Plant reliability investment teams need to champion the shift, ensuring that maintenance engineers and technicians are trained not just on the new tools, but on the new processes. They must learn to trust the data and act on the prediction before the visible failure occurs.
Success in PdM hinges on moving beyond a pilot project and making it an integrated part of the industrial culture. It’s an evolution, not a single installation.
Strategic Approach to Deployment
The most effective way to implement industrial predictive maintenance is not to try and instrument the entire plant at once. A better strategy involves a phased rollout:
Identify Critical Assets: Start with the most business-critical, high-cost, or high-risk pieces of equipment, those whose failure would cause the most expensive downtime.
This focused approach delivers quick wins and builds the internal support necessary for full digital transformation.
Pilot Program: Implement the system on a small, manageable scale to prove the ROI and work out any technical kinks in the specific operating environment.
Scale and Integrate: Once the pilot is successful, gradually expand the deployment across other asset classes, integrating the maintenance data with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) software.
This focused approach delivers quick wins and builds the internal support necessary for full digital transformation.
Conclusion
The future of manufacturing is digital and predictive. Predictive maintenance isn’t optional anymore; it’s essential for staying efficient and competitive. It turns operations from reactive to smart, boosting reliability and reducing costs. With IoT and analytics, companies can operate more safely, efficiently, and cost-effectively. In Industry 4.0, investing in predictive maintenance is the smart move now.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
1. Why is predictive maintenance important for industry?
Predictive maintenance is important for the industry because it helps detect equipment issues before failure, reduces downtime, and increases overall productivity. It allows companies to shift from reactive repairs to data-driven maintenance, saving time and operational cost.
-
2. How predictive maintenance drives industrial growth?
Predictive maintenance drives industrial growth by improving equipment uptime, optimizing resource usage, and enhancing production efficiency. It enables industries to scale operations without frequent breakdowns or unexpected maintenance interruptions.
-
3. What are the benefits of predictive maintenance in manufacturing?
The benefits of predictive maintenance in manufacturing include improved machine reliability, reduced maintenance costs, fewer production stoppages, and a longer lifespan for equipment. It also supports continuous improvement and lean manufacturing goals.
-
4. How does predictive maintenance for industrial equipment work?
Predictive maintenance for industrial equipment works by using sensors, real-time data, and analytics to monitor equipment health. It identifies patterns that indicate future failures, allowing technicians to schedule maintenance only when needed
-
5. What are AI-powered predictive maintenance systems?
AI-powered predictive maintenance systems use machine learning and artificial intelligence to analyze equipment data, predict failures earlier, and automate decision-making. These systems deliver higher accuracy than traditional maintenance models and help industries improve efficiency.
📅 Posted by Nirav Thakkar on November 25, 2025
Nirav Thakkar
Semiconductor Fab Automation & Equipment Software specialist with 18 years of industry experience.

